

Interactive: Hydrogen Bonding: Explore hydrogen bonds forming between polar molecules, such as water. As in a molecule where a hydrogen is attached to nitrogen, oxygen, or fluorine, the electronegative atom attracts the electron cloud from around the hydrogen nucleus and, by decentralizing the cloud, leaves the hydrogen atom with a positive partial charge. Diethyl ether contains an oxygen atom that is a hydrogen bond acceptor because it is not bonded to a hydrogen atom and so is slightly negative.Ī hydrogen attached to carbon can also participate in hydrogen bonding when the carbon atom is bound to electronegative atoms, as is the case in chloroform (CHCl 3). Hydrogen bond donor and hydrogen bond acceptor: Ethanol contains a hydrogen atom that is a hydrogen bond donor because it is bonded to an electronegative oxygen atom, which is very electronegative, so the hydrogen atom is slightly positive. The diethyl ether molecule contains an oxygen atom that is not bonded to a hydrogen atom, making it a hydrogen bond acceptor. Greater electronegativity of the hydrogen bond acceptor will create a stronger hydrogen bond.

An electronegative atom such as fluorine, oxygen, or nitrogen is a hydrogen bond acceptor, regardless of whether it is bonded to a hydrogen atom or not.
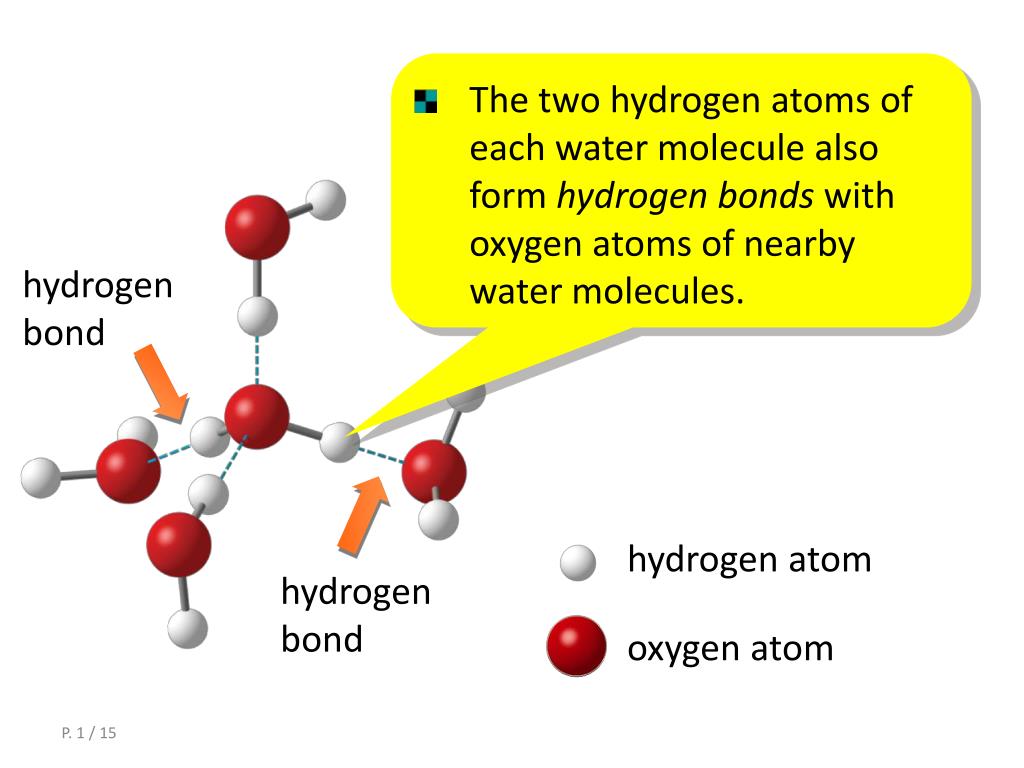
\)Ī hydrogen bond is a strong intermolecular force created by the relative positivity of hydrogen atoms.Ī hydrogen bond results when this strong partial positive charge attracts a lone pair of electrons on another atom, which becomes the hydrogen bond acceptor.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
